Stress fracture of the metatarsal
A stress fracture is a small crack that appears in a bone as a result of repetitive stress. Stress fractures are commonly found in the metatarsals (the long bones that connect the middle of the foot to the toes) and can be a great source of pain. It is important to visit a podiatrist if you think you have a stress fracture, because the sooner it is treated the better the chance it has of healing quickly and you can resume your normal activity.
The metatarsals are a set of five long, thin bones that connect the ankle and tarsal bones to the toes. The metatarsals have an important role in foot function; this is because the metatarsals act as shock absorbers, absorbing our body weight which is transferred through the foot with every step. The metatarsals also help form two of the arches in the foot, and as a result they act as stabilizers. The metatarsals are therefore subject to great forces and are particularly susceptible to a stress fracture.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is also sometimes referred to as a March fracture. This is because stress fractures of the metatarsal were often found in soldiers due to the amount of marching they were required to do.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is essentially an overuse injury that is typically seen in those who participate in high impact sports. Unlike an actual 'break' in the bone, which divides the bone and occurs as a result of trauma, a stress fracture is more like a small crack that has appeared due to repetitive stress; hence the name 'stress fracture'.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is most often seen in the second metatarsal.
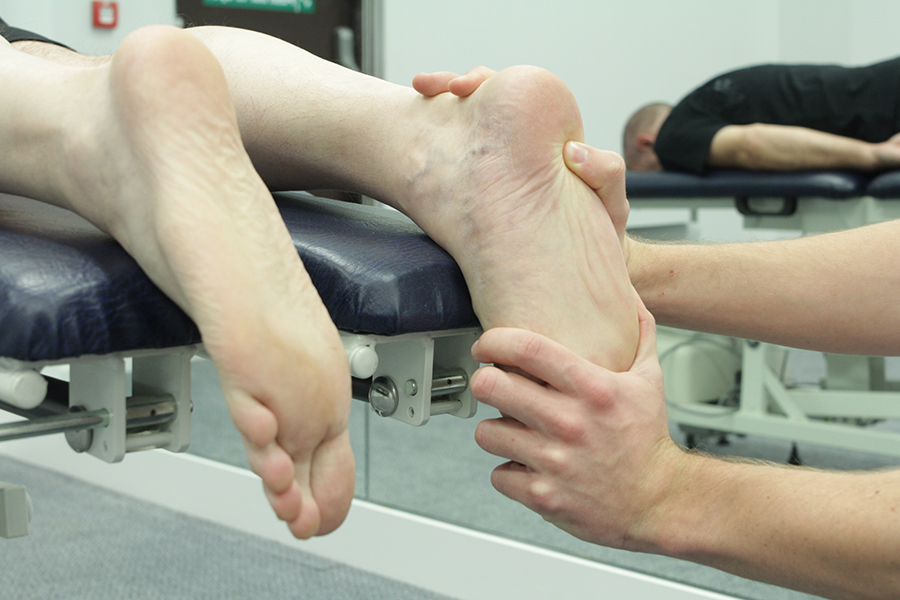
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is an overuse injury caused by the bone being put under great stress over a long period of time, which weakens the bone predisposing it to fracture. The reason for this is that when the foot is put under a great amount of stress over a long period of time the muscles tire and stiffen. When the muscles stiffen this has a direct impact on the function of the metatarsals, because this is where a number of muscles connect. The result is that the metatarsals do not work efficiently as shock absorbers and cracks begin to appear. If the body is given sufficient time to recover these cracks will heal, however continuing to put the area under stress will weaken the bone and cause it to fracture.
Other contributing factors of a metatarsal stress fracture Include:
The signs and symptoms of a metatarsal stress fracture include:
An examination and thorough history are important in the diagnosis of a metatarsal stress fracture. X-ray is not always suitable as stress fractures do not always show up on an X-ray.
If you have a stress fracture of the metatarsal you will benefit from in intervention at Chiropody.co.uk. Benefits include:
Podiatric intervention might also include prescriptive exercises, joint mobilisation, and lipus. Exercises strengthen muscles, which then support the bones, reducing the risk of future injury, whilst lipus increases the healing rate of the fracture.
If you think you have a stress fracture of the metatarsal please visit Chiropody.co.uk for an assessment.
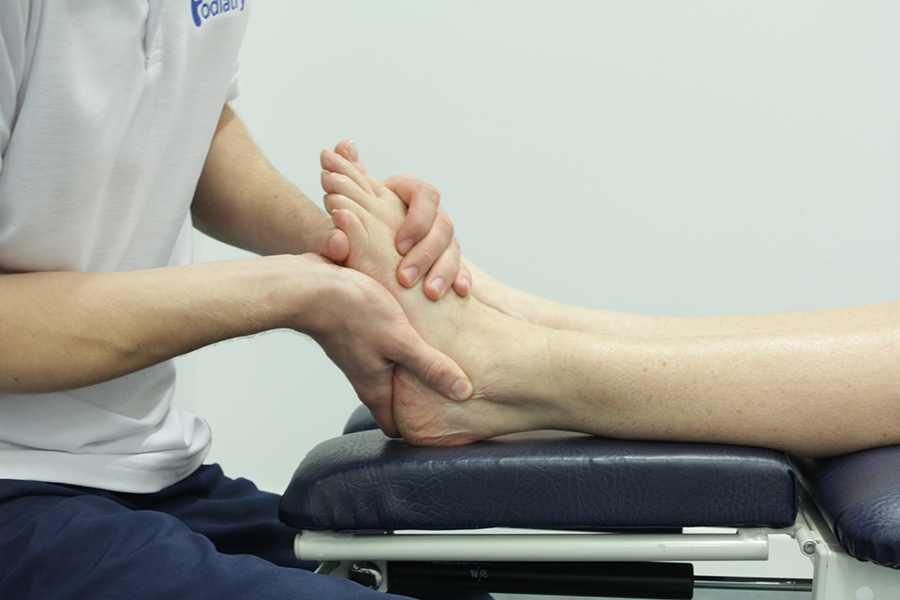
Your podiatrist will first obtain from you a thorough medical and social history, as well as a history of the problem. The history along with an examination of the area affected will help the podiatrist come to a diagnosis. If poor biomechanics are the problem then you may be referred for a biomechanical assessment
If you do have a metatarsal stress fracture treatment will include:
A stress fracture of the metatarsal, or March fracture as it is also known, is an overuse injury. Stress fractures are small cracks that appear in the bone due to repetitive stress, because of this they are commonly seen in athletes or those who participate in high impact sports.
The metatarsals are vulnerable to stress fractures because they are the bones that help to absorb shock. The metatarsals are also stabilizers of the foot.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal can be very painful and tender, if you have a stress fracture you should avoid putting weight on it so that it can be allowed to heal.
If you have a stress fracture you should visit a podiatrist. Your podiatrist will be able to offer both advice and treatment that will aim to aid healing and prevent further trauma.
To arrange an assessment with one our podiatrists please email office@chiropody.co.uk or call 0330 088 4222.
What is a stress fracture of the metatarsal?
The metatarsals are a set of five long, thin bones that connect the ankle and tarsal bones to the toes. The metatarsals have an important role in foot function; this is because the metatarsals act as shock absorbers, absorbing our body weight which is transferred through the foot with every step. The metatarsals also help form two of the arches in the foot, and as a result they act as stabilizers. The metatarsals are therefore subject to great forces and are particularly susceptible to a stress fracture.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is also sometimes referred to as a March fracture. This is because stress fractures of the metatarsal were often found in soldiers due to the amount of marching they were required to do.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is essentially an overuse injury that is typically seen in those who participate in high impact sports. Unlike an actual 'break' in the bone, which divides the bone and occurs as a result of trauma, a stress fracture is more like a small crack that has appeared due to repetitive stress; hence the name 'stress fracture'.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is most often seen in the second metatarsal.

What causes a stress fracture of the metatarsal?
A stress fracture of the metatarsal is an overuse injury caused by the bone being put under great stress over a long period of time, which weakens the bone predisposing it to fracture. The reason for this is that when the foot is put under a great amount of stress over a long period of time the muscles tire and stiffen. When the muscles stiffen this has a direct impact on the function of the metatarsals, because this is where a number of muscles connect. The result is that the metatarsals do not work efficiently as shock absorbers and cracks begin to appear. If the body is given sufficient time to recover these cracks will heal, however continuing to put the area under stress will weaken the bone and cause it to fracture.
Other contributing factors of a metatarsal stress fracture Include:
- Rapid increase in mileage
- Increase in training without proper training and conditioning
- Poor biomechanics (leading to overloading of certain metatarsals)
- Trainers with poor shock absorption
- If you have a condition that affects the density of bone (e.g. osteoporosis)
What are the signs and symptoms of a stress fracture of the metatarsal?
The signs and symptoms of a metatarsal stress fracture include:
- The area may be tender to touch
- Pain in the foot that is relieved by rest at first, but eventually the pain is present even when resting
- swelling
How is a stress fracture of the metatarsal diagnosed?
An examination and thorough history are important in the diagnosis of a metatarsal stress fracture. X-ray is not always suitable as stress fractures do not always show up on an X-ray.
Benefits of podiatry for a stress fracture of the metatarsal
If you have a stress fracture of the metatarsal you will benefit from in intervention at Chiropody.co.uk. Benefits include:
- Quicker healing time
- Improvement in shock absorption
- Reduced inflammation
- Reduced pain
- Improvement in gait
- Improvement in foot and lower limb function
- Reduced future injury risk
Podiatric intervention might also include prescriptive exercises, joint mobilisation, and lipus. Exercises strengthen muscles, which then support the bones, reducing the risk of future injury, whilst lipus increases the healing rate of the fracture.
If you think you have a stress fracture of the metatarsal please visit Chiropody.co.uk for an assessment.

What would podiatry for a stress fracture of the metatarsal involve?
Your podiatrist will first obtain from you a thorough medical and social history, as well as a history of the problem. The history along with an examination of the area affected will help the podiatrist come to a diagnosis. If poor biomechanics are the problem then you may be referred for a biomechanical assessment
If you do have a metatarsal stress fracture treatment will include:
- Rest ' this is very important. You must not work through the pain, doing this could cause the metatarsal to break
- Anti-inflammatory advice
- Orthoses
- Lipus
- Strengthening Exercises
- Stretching Programmes
- Footwear review
- Strapping
- Padding
Summary
A stress fracture of the metatarsal, or March fracture as it is also known, is an overuse injury. Stress fractures are small cracks that appear in the bone due to repetitive stress, because of this they are commonly seen in athletes or those who participate in high impact sports.
The metatarsals are vulnerable to stress fractures because they are the bones that help to absorb shock. The metatarsals are also stabilizers of the foot.
A stress fracture of the metatarsal can be very painful and tender, if you have a stress fracture you should avoid putting weight on it so that it can be allowed to heal.
If you have a stress fracture you should visit a podiatrist. Your podiatrist will be able to offer both advice and treatment that will aim to aid healing and prevent further trauma.
To arrange an assessment with one our podiatrists please email office@chiropody.co.uk or call 0330 088 4222.
Save 5% by booking an appointment online.

Find your nearest clinic
We have clinics located throughout the North West. We also provide a home visit service.
Find out more »
No waiting lists!
Tired of waiting for treatment? Be seen by a podiatrist today!
Find out more »

Not sure how we can help?
Speak to a podiatrist to find out how we can help. Call us on 0330 088 4222.
Find out more »
We work with:

Individuals

Organisations

Health professionals
Get in Touch!
0330 088 4222
If you would like to speak to one of our specialists then please complete this form.
We are open 7 days a week