Inferior tibiofibular joint injury
An inferior tibiofibular joint injury describes a painful injury affecting
the front of the ankle. Inferior tibiofibular joint injuries occur when the
tibia and fibular, which are the two long bones that form the lower leg are
forced apart.
Podiatrists assess, diagnose and treat a variety of lower limb injuries.
Podiatric intervention for a tibiofibular joint injury at Chiropody.co.uk
may include prescription orthoses, stretching programmes, strengthening
exercises, proprioceptive exercises and joint mobilisation.
What is an inferior tibiofibular joint injury?
An inferior tibiofibular joint injury is an injury that can appear following a severe twisting of the ankle. When the ankle is twisted it can place a great amount of stress on the tissue that connects the tibia and the fibula (the two bones that form the lower leg), which causes the tissue to tear. The result of an inferior tibiofibular joint injury is pain, which can range from mild to severe depending on the degree of injury, making weight bearing and other activities that require two feet difficult.
What causes an inferior tibiofibular joint injury?
An inferior tibiofibular joint injury is typically the result of a severe twisting of the ankle; this is the position the ankle is in when the foot is pointing inwards. Inferior tibiofibular joint injuries are mostly seen following severe ankle sprains, this is because in order for the tibia and fibular to be forced apart the force acting on them must be great.
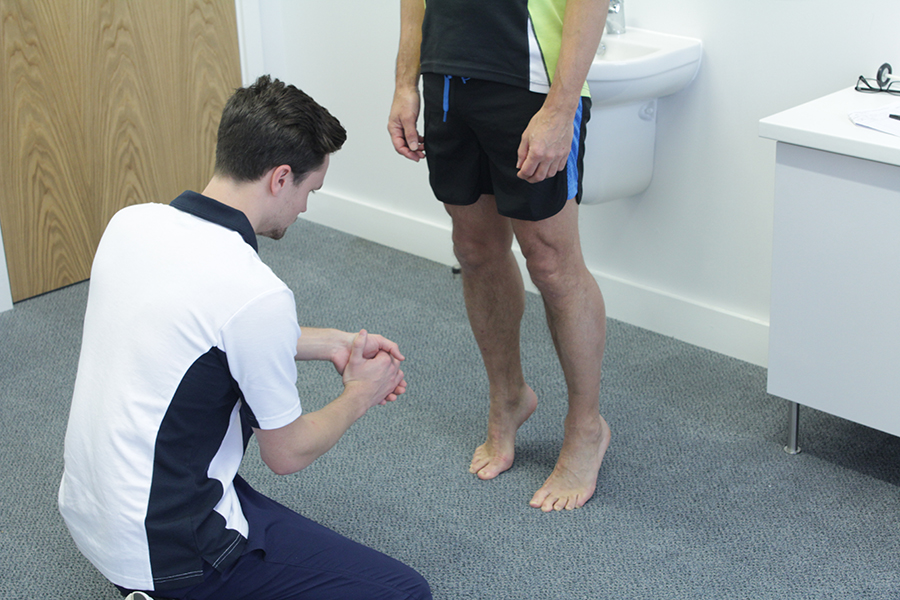
What are the signs and symptoms of an inferior tibiofibular joint injury?
The signs and symptoms of an inferior tibiofibular joint injury is sudden pain at the front of the ankle following severe inversion of the ankle. The ankle may be swollen and bruised and you will find it difficult to bear weight. Pain may increase upon palpation of the tibiofibular joint.
How are inferior tibiofibular joint injuries diagnosed?
An inferior tibiofibular joint injury can be diagnosed at Chiropody.co.uk following a subjective and objective assessment. An x-ray may be required to confirm the diagnosis of inferior tibiofibular joint injury and to rule out fracture.
Benefits of podiatry for inferior tibiofibular joint injury
If you have an inferior tibiofibular joint injury podiatry may benefit you
following immobilisation and physiotherapy intervention.
Podiatry can help you with the provision orthoses combined with a heel
lift, proprioceptive exercises, strengthening exercises, and ankle joint
mobilisation. The benefits of podiatric intervention following an inferior
tibiofibular joint are:
Increased ankle range of motion, particularly dorsiflexion (the position
the ankle is in when the toes are pointing upwards).
- Improved ankle strength
- Improved balance
- Improved leg, ankle and foot function
- Decrease in pain
Following immobilisation with a cast or other fixating device the ankle
will become stiff, orthoses and manipulation reduce this stiffness, thereby
increasing flexibility, reducing pain and improving gait, as well as to
improve the congruency of the ankle joint.
Strengthening and proprioceptive exercises will be provided in order to
improve the strength of the ankle and to improve balance. Proprioceptive
and strengthening exercises are important following an inferior
tibiofibular joint injury because they help to strengthen the ankle. Ankle
strengthening is extremely important because often, following an inferior
tibiofibular joint injury the deltoid ligament, which is a strong ligament
on the outside of the foot responsible for ankle stability has been
stretched.
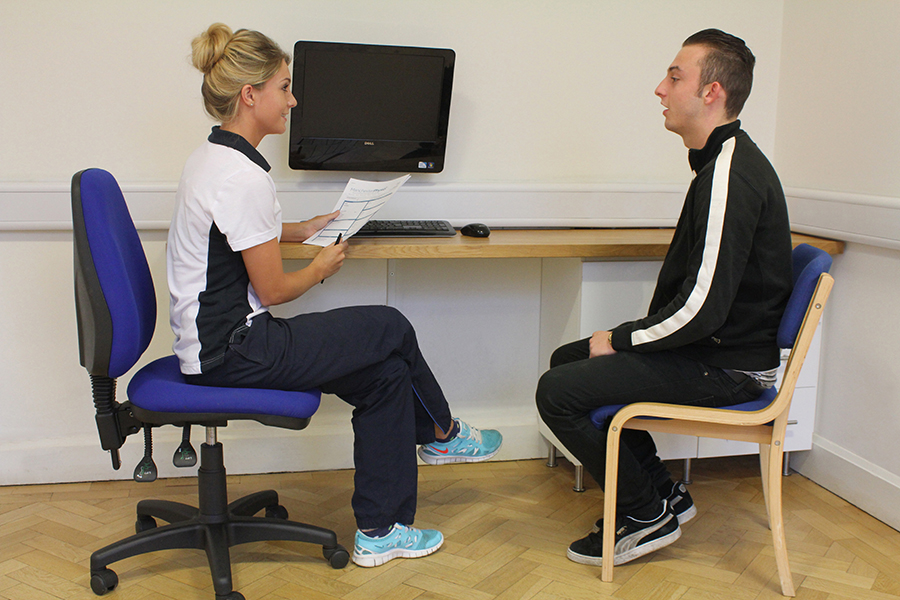
What would podiatry for an inferior tibiofibular joint injury involve?
If you have had an inferior tibiofibular join injury Chiropody.co.uk can
help you. At Chiropody.co.uk we begin each initial assessment with a
thorough history taking. The history is important as it provides vital
clues that aid both diagnosis and treatment. The history is then followed
by a biomechanical assessment, the purpose of which is to assess the
mechanics of your ankle and lower limb and assess muscle strength/weakness.
The results of the biomechanical assessment will then inform the treatment
plan, which will be specific to you. If you require orthoses an impression
of your foot will be taken. All findings and treatment options will be
explained fully.
Treatment for inferior tibiofibular joint injury may include one or more of
the following:
- Orthoses
- Manipulation
- Joint mobilisation
- Strengthening Exercises
- Stretching Programmes
- Proprioception exercises
- Advice and education
- Footwear review
Summary
An inferior tibiofibular joint injury describes an injury to the front of
the ankle in which the tibia and fibular are forced apart. An inferior
tibiofibular joint injury typically follows a severe inversion ankle
sprain. If you have suffered an inferior tibiofibular joint injury podiatry
may benefit you following any appropriate immobilisation and/or
physiotherapy. At Chiropody.co.uk we are specialists in the leg and foot,
we will assess your ankle and provide you with a treatment plan designed to
reduce any pain, improve the mechanics of the ankle and foot, and increase
its strength and flexibility. The results of podiatric treatment following
an inferior tibiofibular joint injury are a reduction in symptoms, improved
gait and posture and prevention of future injury.
If you would like to book an appointment with us at Chiropody.co.uk, Email office@chiropody.co.uk or call 0330 088 4222.
Save 5% by booking an appointment online.


We work with:

Individuals

Organisations

Health professionals
Get in Touch!
0330 088 4222
If you would like to speak to one of our specialists then please complete this form.
We are open 7 days a week