Osgood shlatters disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an overuse injury that affects the growth plate at the tibial tuberosity, which is a bony bump at the top of the leg just below the knee. Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition associated with growth, it is therefore a condition that affects children and teenagers. If a child has Osgood-Schlatter disease they will experience pain and swelling on the outside of the leg, below the knee.
What is Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a painful condition of the knee that affects
children and teenagers. Typically Osgood-Schlatter disease affects children
between the ages of 10 and 15 who participate in sports, particularly those
that require a lot of use from the quadriceps (the muscles at the front of
the thigh), however it can also affect children who do not play sports as
well.
Osgood-Schlatter disease produces pain just below the knee on the outside,
at a site called the tibial tuberosity. The tibial tuberosity is basically
a bony bump at the top of the tibia (leg bone); this is where the patella
tendon (which holds the knee cap in place) attaches. The patella tendon
extends upwards, surrounds the knee cap, and connects the knee cap to the
quadriceps.
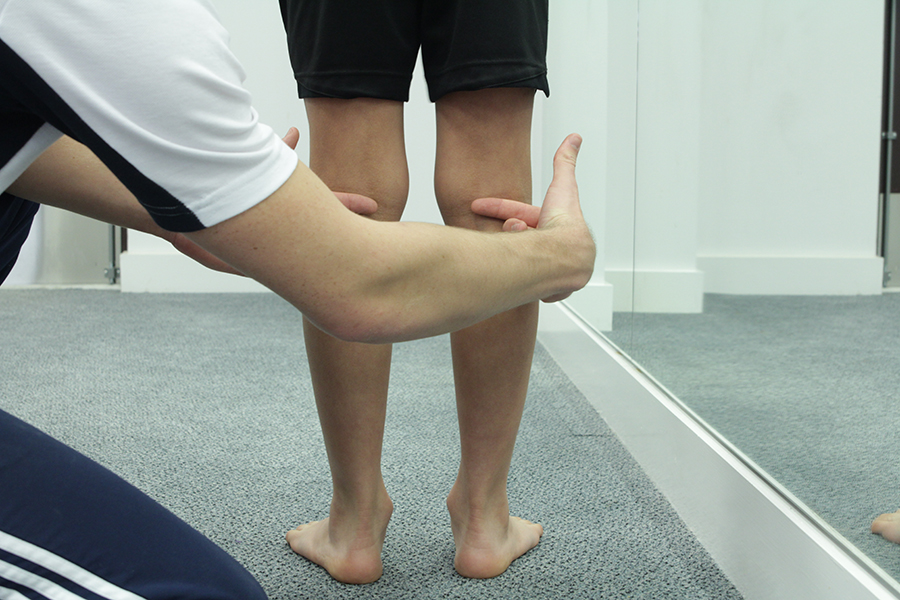
What causes Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is thought to be caused by repeated trauma to the
tibial tuberosity, it is therefore classed as an overuse injury. The reason
that Osgood-Schlatter disease only affects children and teenagers is
because it is associated with growth, secondly, bones that have not
finished growing are relatively soft compared to bones which have completed
their growth, and as result they are more susceptible to injury.
Osgood-Schlatter disease produces pain and inflammation at the tibial
tuberosity, this is because the quadriceps(which attach via the knee cap)
are responsible for straightening the knee. In order for the quadriceps to
be able to straighten the knee they must contract, when the muscle
contracts it pulls at its attachment at the tibial tuberosity. In sports
that require lots of straightening of the leg (e.g. running and jumping
activities) the tibial tuberosity becomes irritated due to the pull of the
quadriceps, which produces pain and swelling, particularly when a child is
experiencing a growth spurt.
What are the signs and symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
The signs and symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease may include:
- Pain below the knee cap, the pain is typically worse during and after activity
- Swelling at the site of pain that may appear as a 'bony bump'
- Appears in children and teenagers aged 10-15. More common in boys.
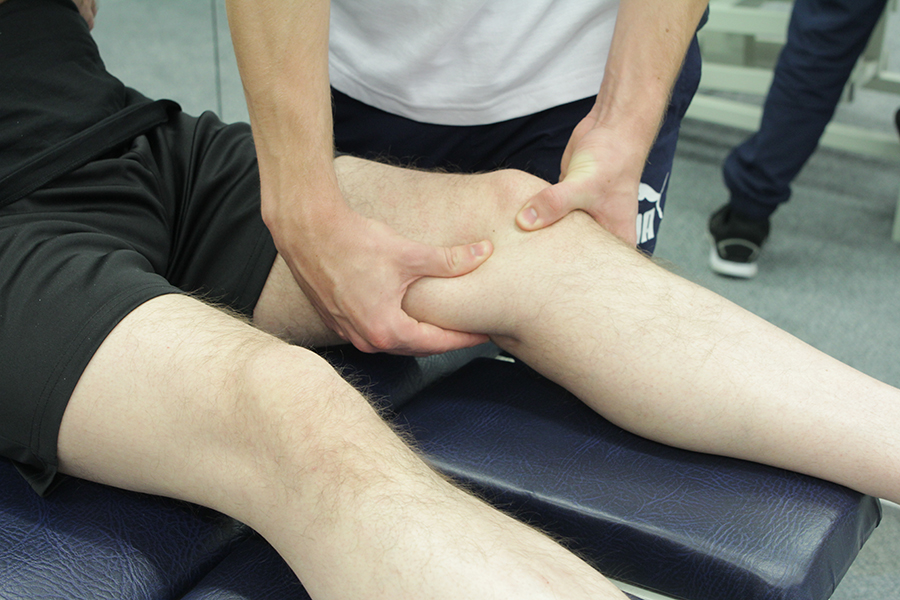
Benefits of podiatry for Osgood-Schlatter Disease:
The benefits of podiatric assessment and treatment for Osgood-Schlatter disease include:
- Decrease in inflammation
- Decrease in pain
- Improvement in lower limb and foot function
- Increase in muscle strength
- Decrease in muscle tightness
- Cause, not just the symptoms treated
Podiatric benefits for Osgood-Schlatter disease are achieved by reducing inflammation and by altering the pull of the quadriceps muscles.
How is Osgood-Schlatter Disease diagnosed?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is diagnosed by a podiatrist. The diagnosis is made based on:
- A medical history
- The signs and symptoms
- An examination
What would podiatry for Osgood-Schlatter Disease involve?
Podiatry for Osgood-Schlatter disease would involve:
- A thorough assessment
- An examination of the knee
Both of which will provide essential clues that will aid the podiatrist in their diagnosis. The next stage of the consultation involves an assessment, which includes:
- An examination
- A biomechanical assessment and gait analysis
The gait analysis and biomechanical assessment will tell the podiatrist how
the foot and leg are functioning. The podiatrist will then use this
information to devise a treatment plan that will aim to reduce the pain and
symptoms that your child is experiencing.
Once a diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease has been confirmed the
following treatment options may be recommended:
- R.I.C.E: rest, ice, compression, elevation
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Orthoses
- Strengthening Exercises
- Stretching Programmes
- Advice and education
- Footwear review
The aim of treatment for Osgood-Schlatter disease is to reduce any pain and inflammation, and to reduce the pull/force being exerted on the knee.
Summary
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a painful condition of the knee that affects
the growth plate of the tibial tuberosity. The tibial tuberosity is a bony
bump at the top of the leg just below the knee; this is where the tendon
that connects the quadriceps to the knee attaches.
Osgood-Schlatter disease affects children and teenagers, typically those
between the ages of 10 and 15. Osgood-Schlatter disease is associated with
playing sports and is therefore classed as an overuse injury; however,
children who do not participate in sports may still be affected.
If you think your child has Osgood-Schlatter disease visit one of our
podiatrists who will be able to help alleviate the painful symptoms
associated with the condition.
To arrange an assessment with one our podiatrists please email office@chiropody.co.uk or call 0330 088 4222.
Save 5% by booking an appointment online.


We work with:

Individuals

Organisations

Health professionals
Get in Touch!
0330 088 4222
If you would like to speak to one of our specialists then please complete this form.
We are open 7 days a week