Tibialis posterior tendinopathy
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is a painful and degenerative condition
that affects the tibialis posterior tendon. The tibialis posterior tendon
comes from the tibialis posterior muscle, which is at the back of the leg.
Its tendon courses behind the inside of the ankle bone and attaches beneath
the foot. The pain experienced in tibialis posterior tendinopathy may be
felt anywhere along the tibialis posterior tendon, standing on tip toes can
be particularly painful.
If you have tibialis posterior tendinopathy visit us at Chiropody.co.uk.
Our podiatrists are highly trained in a variety of conditions affecting the
foot and leg. Following an assessment, the podiatrists at Chiropody.co.uk
will diagnose your condition and provide you with an appropriate treatment
plan.
What is tibialis posterior tendinopathy?
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is a painful condition that affects the muscle at the back of the leg known as the tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior muscle courses down the back of the leg, with its tendon running behind the inside of the ankle bone before inserting into a bone on the inside of the foot called the navicular, as well as beneath metatarsals two to five. Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is associated with overuse; it is therefore most often seen in athletes. The pain associated with posterior tibialis posterior is the result of degeneration of the tendon.
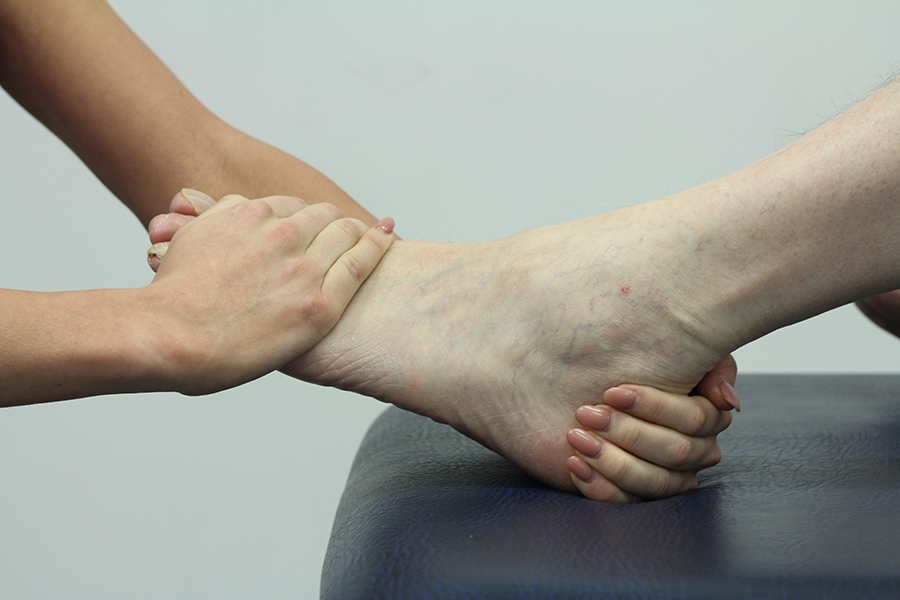
What causes tibialis posterior tendinopathy?
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is typically the result of overuse, which
causes the tendon to weaken and break down. People whose feet over-pronate
(the feet flatten and the ankles roll inward), or those who must evert the
foot (point the foot outwards, as observed in skating, are more susceptible
to tibialis posterior tendinopathy.
Tibialis posterior tendionopathy can also be caused by injury to the
tendon.
What are the signs and symptoms of tibialis posterior tendinopathy?
In the beginning stages of posterior tibial tendionopathy there may be
swelling and pain and an aching that follows the course of the tendon. The
posterior tibial tendon eventually weakens and you may find it difficult to
balance. Finally, the inside arch of the foot will collapse or 'flatten'
and when this happens pain is often felt on the outside of the ankle,
caused by the heel bone catching on the ankle. The reason the arch
progressively flattens is because the tibialis posterior tendon has a role
in supporting the arch of the foot, when the tendon weakens it is unable to
do its job.
Tibialis posterior problems typically present where the tendon courses
behind the medial malleolus (the inner ankle bone). This is because this
part of the tendon has the weakest blood supply, which means that the
necessary blood required for healing the tendon is not delivered.
How is tibialis posterior tendinopathy diagnosed?
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy can be diagnosed quite quickly by the podiatrists at Chiropody.co.uk following a thorough assessment. The tibialis posterior does most of its work during the contact phase of the gait cycle (this is when the heel touches the ground), therefore, any problem caused by the posterior tibial tendon requires a biomechanical assessment in order to assess the mechanics of the foot both weight bearing, non-weight bearing and during gait.
Benefits of podiatry for tibialis posterior tendinopathy
If you have tibialis posterior tendinopathy podiatry can help you. All most every case of tibialis posterior tendinopathy occurs when the heel first contacts the ground, due to the great amount of stress being exerted at this point. It is essential that the ankle is strong and that any excessive stress is controlled. The benefits of podiatry treatment for tibialis posterior tendinopathy are:
- Reduction in pain
- Improved mechanics of the leg, ankle and foot
- Improved gait and posture
Orthoses may be prescribed if you have tibialis posterior tendinopathy.
Orthoses are shoe inserts that control forces, allowing the foot to
function so that stress is taken away from painful structures. The benefit
of orthoses for tibialis posterior tendinopathy is a reduction in pain and
an improvement in the mechanics of the leg and foot, which directly has an
effect on gait and posture.
Advice and education will be given at your podiatry consultation,
particularly with regards footwear. It is essential that if you have
posterior tibial tendon dysfunction that you are wearing the correct
footwear, particularly when participating in sports. The benefits of good
shock absorption should not be ignored, and the podiatrists at
Chiropody.co.uk will be able to advise you on this.
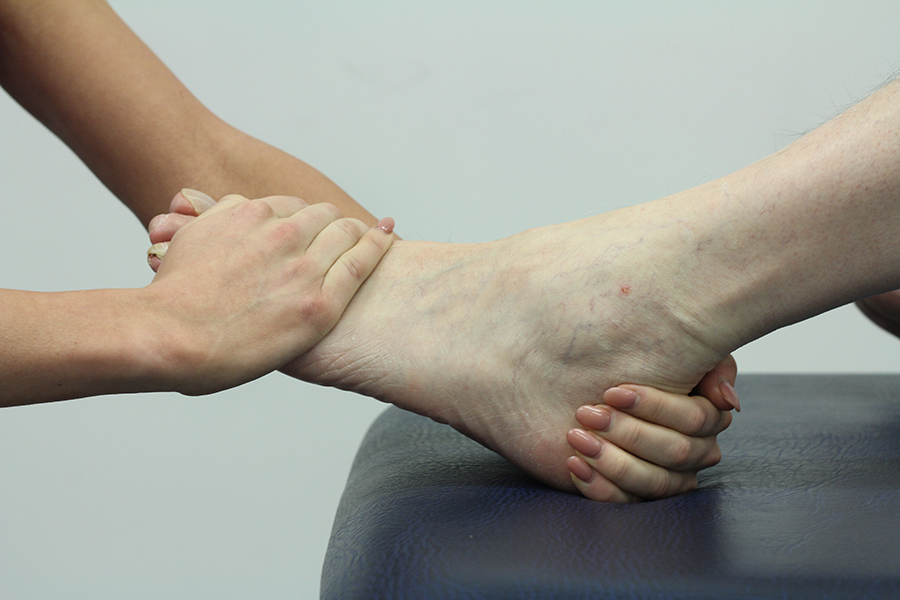
What would podiatry for tibialis posterior tendinopathy involve?
At Chiropody.co.uk we obtain a thorough history at the initial appointment, this includes:
- Medical history
- History of the presenting problem
- Occupation
- Sporting activities
- History of injury
- Signs and symptoms
- Biomechanical assessment
The history is the starting point and will provide the podiatrist with important information that will aid their diagnosis. Following the history, the podiatrist will then assess you, which is done via a biomechanical assessment and gait analysis. All treatments for tibialis posterior tendinopathy are specific to the individual, but may include one, or a combination of the following:
- Orthoses
- Strengthening exercises
- Strengthening programme
- Balance exercises
- Footwear review
- Acupressure
- Manual therapy
- Trigger point therapy
- Ultrasound
- Training review
- Advice and education
- Manipulation / mobilisation
- Massage
- Myofascial release
- Soft tissue mobilisation
The purpose of treatment for tibialis posterior tendinopathy is to improve your painful symptoms and to improve the mechanics and function of the leg ankle and foot.
Summary
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is a painful condition that affects the
tibialis posterior tendon, producing pain and discomfort along its course
and a progressive 'flattening' of the foot. Tibialis posterior tendinopathy
is associated with overuse, poor biomechanics and activities that require
the foot to evert more than usual (e.g. skating).
If you have tibialis posterior tendinopathy it is important that it is
treated, in order to prevent further deterioration of the tendon.
To arrange an appointment at Chiropody.co.uk office@chiropody.co.uk or call 0330 088 4222.
Save 5% by booking an appointment online.


We work with:

Individuals

Organisations

Health professionals
Get in Touch!
0330 088 4222
If you would like to speak to one of our specialists then please complete this form.
We are open 7 days a week